 |
submitted by /u/techcouncilglobal [link] [comments] |
Category: Chat
-
Gab
-
Voice Assistant Use Case – Health and Wellness

With cutting-edge artificial intelligence upgrading our lives above mediocrity, voice technology emerges out to be the healthcare stalwarts of the future. From handling follow-up calls to medical triage, booking appointments, and even diagnosis, VUI (Voice User Interface) is the perfect combination of medical knowledge with technology and tones of conversation to be the voice of the healthcare industry.
To prevent the spread of COVID-19 and to continue responding to healthcare needs, hospitals are rapidly adopting telehealth and other digital health tools to deliver care remotely. Intelligent conversational agents and virtual assistants, such as chatbots and voice assistants, have been utilized to augment health service capacity to screen symptoms, deliver healthcare information, and reduce exposure. In this commentary, we examined the state of voice assistants (e.g., Google Assistant, Apple Siri, Amazon Alexa) as an emerging tool for remote healthcare delivery service and discussed the readiness of the health system and technology providers to adapt voice assistants as an alternative healthcare delivery modality during a health crisis and pandemic.

In this fast-moving world, people tend to ignore a very basic part of their lives, their health. We at Voxogenic Technologies believe in the old adage, ‘Health is Wealth’. A voice assistant for general health and wellness seemed like the perfect answer to counter this. It can tackle the following use cases:

The user can make use of the voice assistant to act as their personal trainer. By mixing and matching a set of customized exercises, the user can create their very own workout routine and the voice assistant to repeat them. E.g. ‘Alexa, start my daily workout routine.’ ‘You have 3 workout routines, which one would you like to choose for today?’

The user can ask the voice assistant to calculate their B.M.I. by gathering some basic information about the user. It can also store the data, set a target for the user’s ideal B.M.I., and help you keep track of your progress.

Trending Bot Articles:
1. How Chatbots and Email Marketing Integration Can Help Your Business
Booking an appointment has never been this effortless. Now the user can book a doctor’s appointment, ask for recommended doctors in the area, and more.

The trick is to make this as easy as possible for the patient. Just like the patient beds in hospitals are equipped with a button, the voice assistant can work as the button without the need to look for a button.

In a smart hospital ward, the user will have the option to control the electrical appliances without having the hassle to move around or finding the remote.
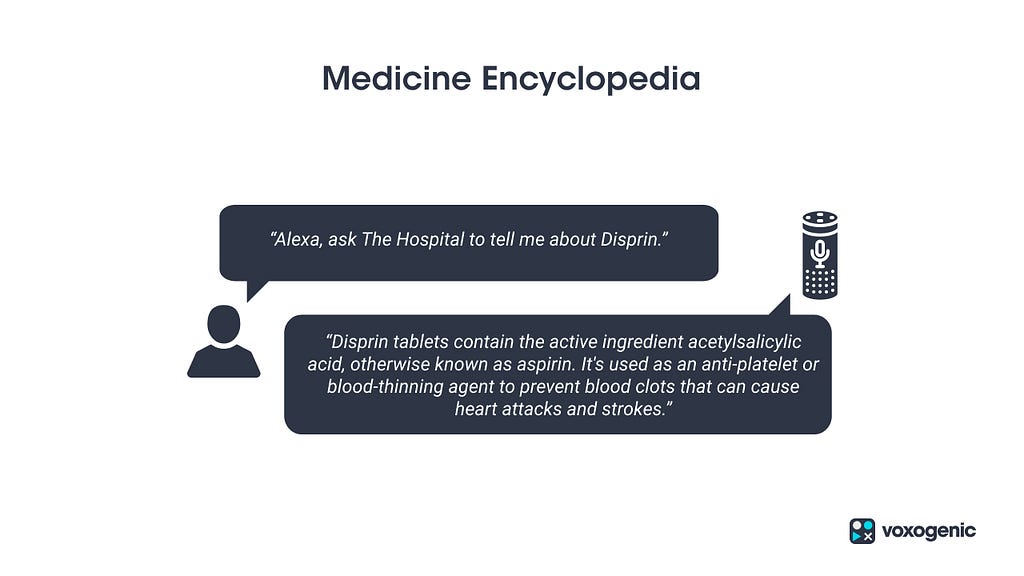
A user may have multiple ailments for which the doctor may have prescribed multiple medicines. It will be up to the voice assistant to keep the user informed about which medicine to take when. E.g ‘Alexa, which medicine should I take for a common cold?’ ‘The doctor has prescribed you Wikoryl for your cold.’

The user may forget to take a medicine or two due to some factor or the other. This can be minimized by giving the user the option to set reminders for the daily medication.
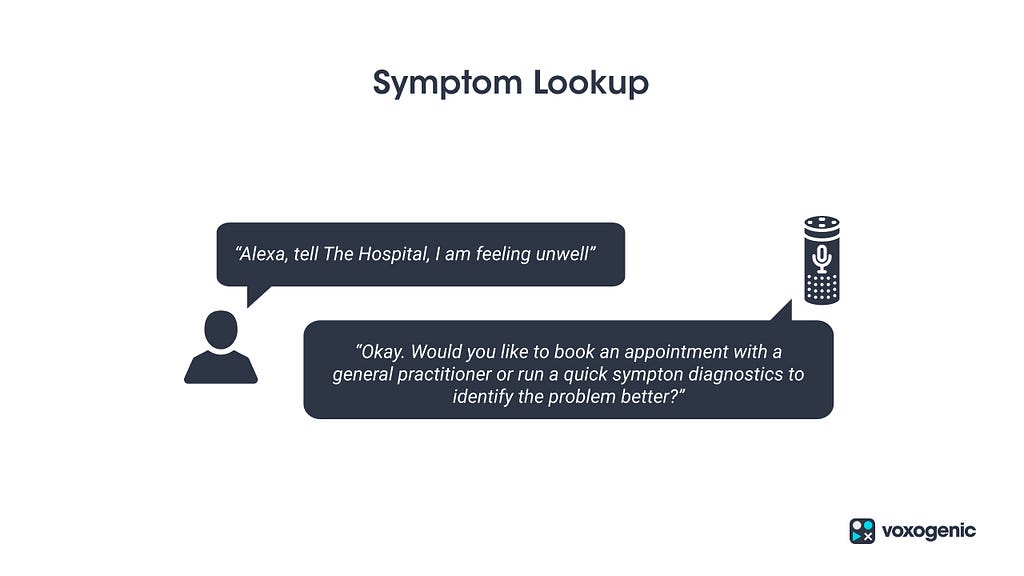
In this use case, the user won’t be prescribed medicines but rather act as a pre-screening to potential disease. The user will be able to get help regarding their symptoms from the voice bot.

The voice assistant can act as an answer hub for all the queries. The user may ask questions regarding the availability of doctors, diseases, etc.

The voice bot can help give daily bits of customized information even when the user is not in need of any help. The information can be tailored to match the user’s needs.
A better and improved healthcare industry is on the go to renovate the conventional healthcare modes. Artificial intelligence-backed tools, smart and friendly Alexa, voice apps with medical proficiency are dominating the market. The integration of voice technology with the medical arena can bring about revolutionary changes. From understanding patient behavior to comprehending the effects of the drug, recognizing health emergencies, and setting up appointments, voice technology will lead to a paradigm shift in the present model of the healthcare industry.
So pull up your socks! The next time you receive a follow-up call from a hospital may not be someone of flesh and blood. It may be a chatbot trained to converse with you and give you pills for a happy and healthy life. Talk to one of our representatives to integrate customized voice technology solutions for your business.
If you are looking to build any kind of conversation apps that works through Voice and Chat, please feel free to drop us an email at contact@voxogenic.com
We have expertise in designing and developing Voice applications on Amazon Alexa & Google Home and Chatbots for platforms such as Website, Mobile Apps, Facebook, Twitter, Slack, Line, Skype, and many more.
To know more about us you can visit https://www.voxogenic.com
Don’t forget to give us your 👏 !


Voice Assistant Use Case –
Health and Wellness was originally published in Chatbots Life on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story. -
Build Chatbots for SharePoint using Power Virtual Agents & SPFx
How to build powerful chatbots on Power Virtual Agents(PVA) and then host it on SharePoint using SharePoint Framework (SPFx)

PVA Chatbot in SharePoint in action Introduction
PVA is a new service from Microsoft that just came out of public preview in mid 2020. It allows users to easily build powerful and complex chatbots using a no-code user interface. If used together with SharePoint, it empowers companies to easily build chatbots for their company intranets that can answer employees’ frequently asked questions, find people or documents and more.
This post is a step by step guide on how you can build a chatbot using PVA and host it on SharePoint using SPFx extensions.

Prerequisites
- PVA license (Free Trial available)
- An existing SharePoint Site
- Basic React knowledge
- Node.js v10.x
- SPFx setup (Official Setup Guide)
Step-by-step Guide
1. Creating a bot on PVA & obtain bot ID
Head over to the PVA Portal and follow the on-screen step-by-step instructions to create your PVA bot. In here, you will be able to choose what language you want your bot to understand. Currently, you can only have 1 language per bot.
Trending Bot Articles:
1. How Chatbots and Email Marketing Integration Can Help Your Business
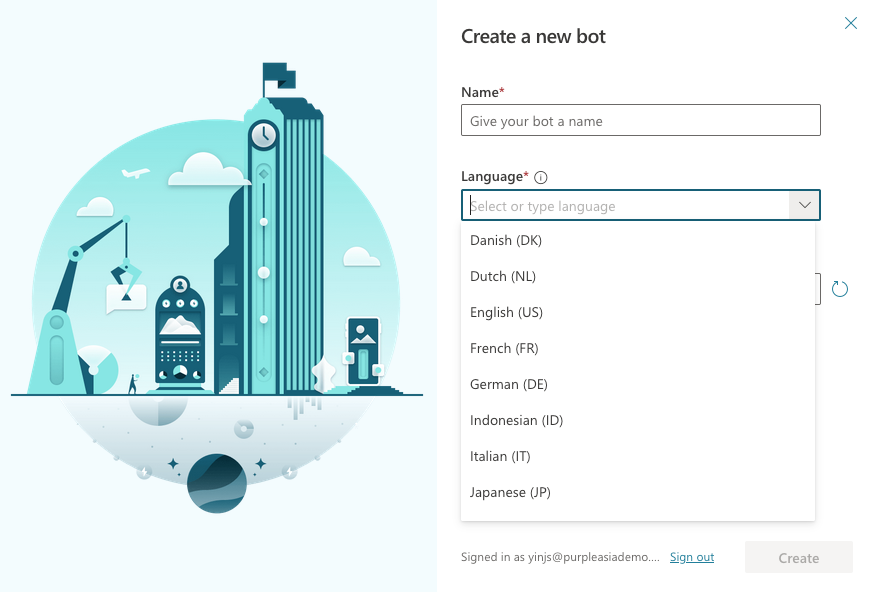
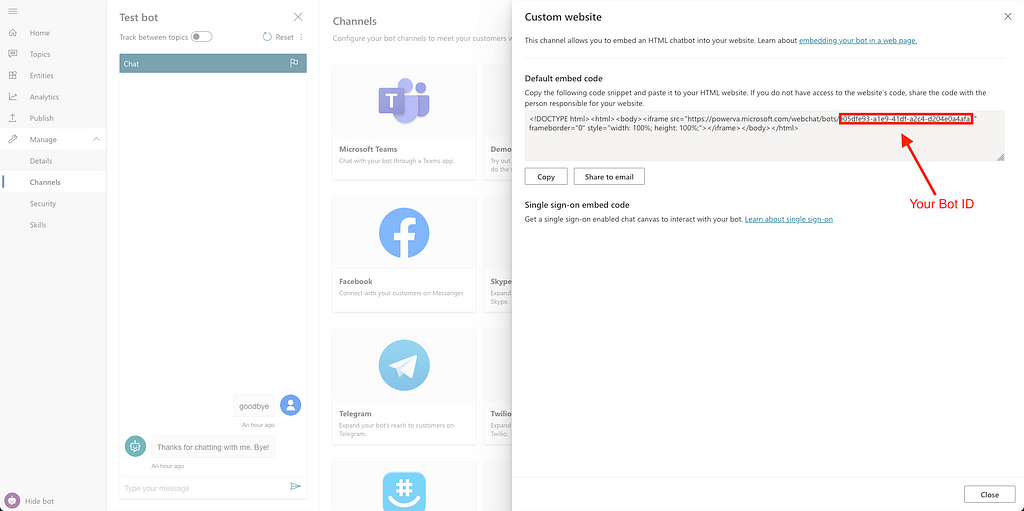
Create new bot popup on PVA From the left panel, select “Manage > Channels” and then select “Custom Website”. Copy the Bot ID and paste it somewhere, we will need it later.
2. Create SPFx extension
We will need to create a SPFx extension in order to host our PVA bot on SharePoint. SPFx extension allows us to deploy our bot to all pages in a single site. If you just want to create a bot in a single page, you can use SPFx web parts instead.
To create a SPFx extension, open your command line and in the folder that you want to create your SPFx extension, run the command below and key in the following values. Feel free to change the name and description to something to your liking.
yo @microsoft/sharepoint
What is your solution name? pva-chatbot
Which baseline packages do you want to target for your component(s)? SharePoint Online only (latest)
Where do you want to place the files? Use the current folder
Do you want to allow the tenant admin the choice of being able to deploy the solution to all sites immediately without running any feature deployment or adding apps in sites? No
Will the components in the solution require permissions to access web APIs that are unique and not shared with other components in the tenant? No
Which type of client-side component to create? Extension
Which type of client-side extension to create? Application Customizer
What is your Application Customizer name? PVAChatbot
What is your Application Customizer description? PVAChatbot descriptionMake sure you are on Node.js v10.x, see the SPFx Extension Getting Started Guide if you are stuck.
3. Modify SPFx Extension to host PVA Bot
Install Bot Framework Web Chat using the command below:
npm install botframework-webchat
Create a “Chatbot.tsx” file in “src/extensions/<project_name>” and paste the following code into the file. Make sure you change the BOT_ID variable on line 25.
Head over to “<project_name>ApplicationCustomizer.ts” file, and paste the code below. This will create a Bottom Placeholder across all your pages in the SharePoint site and within the placeholder, it will render the Chatbot Component that we just created.
4. Serving & testing locally on SharePoint
Head over to “config/serve.json” and change the pageUrl to your own SharePoint site url.
Run the command below to serve locally and test
gulp serve
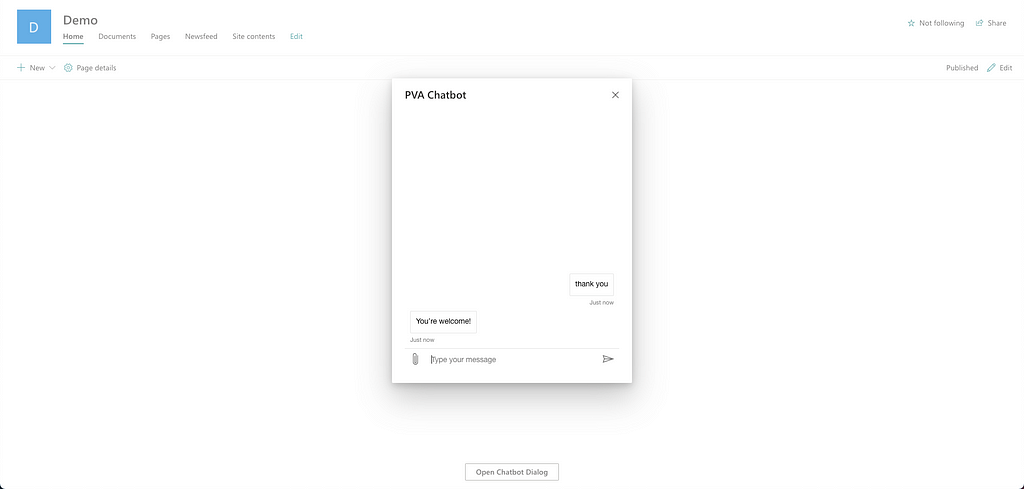
Screenshot of PVA Chatbot in Demo SharePoint site If you see “Unable to connect” error message in the popup window, it means your BOT_ID is incorrect. Double check your BOT_ID on line 25 of the Chatbot.tsx file.
5. Deploy to SharePoint
Run the following commands to build your SPFx extension
gulp bundle --ship
gulp package-solution --shipYou should see a “.sppkg” file being generated in your “sharepoint/solution” folder. Upload this file to your tenant’s SharePoint App Catalog.
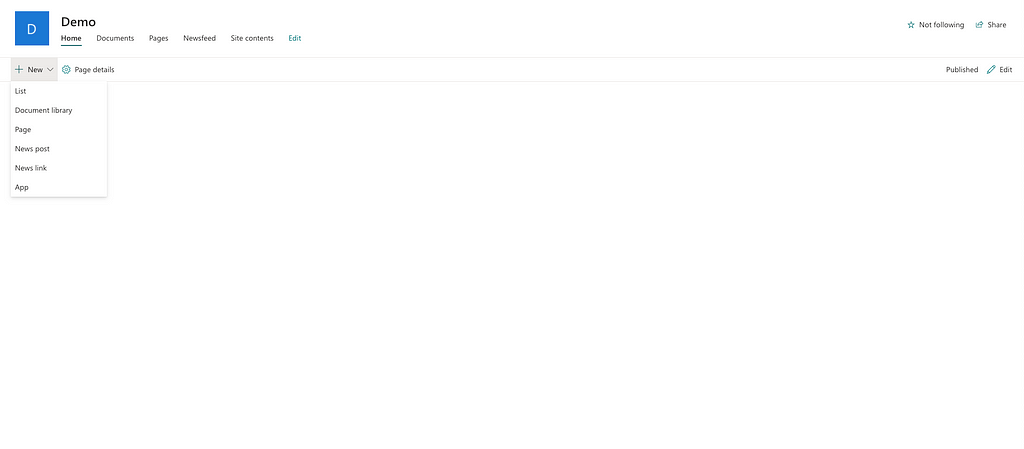
Head over to your SharePoint site that you want to add this Chatbot to. Click on “+ New > App” and then select the newly uploaded extension file and you should see “Open Chatbot” button at bottom of your SharePoint page.
Adding SPFx extension App to SharePoint site Refer to the official SPFx extension deployment guide if you are stuck.
Conclusion
This is only the first step, from there you can extend more functionality to your PVA chatbot. Link it up to Power Automate and you achieve some pretty complex features, such as searching for documents, finding people in Azure AD or even link up to external API via Power Automate connectors.
Want to customise your bot UI on the extension? Want to build more topics on PVA but not sure how? Have more complex use cases but not sure how to build it? Feel free to reach out!
Don’t forget to give us your 👏 !



Build Chatbots for SharePoint using Power Virtual Agents & SPFx was originally published in Chatbots Life on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
-
Virtual Chatbot And Conversational AI Conferences 2021

We will probably still have to do without on-site conferences for the most part in 2021. However, that doesn’t mean there won’t be any interesting conferences and networking events this year.
On the contrary. Many of the events will take place online, so you don’t have to limit your choice based on your location. Check out this blog article for an overview of the most important Chatbot and Conversational AI conferences in 2021.

Which Chatbot And Conversational AI Conferences Shouldn’t Be Missed In 2021?
Chatbot Conference Online — AI, Chatbots, Virtual Assistants And Voice
From topics such as AI in customer service to Conversational AI trends and Best Practices, this conference will provide attendees with exciting real-world insights and food for thought from companies such as Google, IBM and Salesforce.
The most important information about the Chatbot Conference Online at a glance:
- Date: May 25–27, 2021
- Location: Online
- Website: Here you can find more information about the Chatbot Conference Online.
By the way — would you like to learn more about the technology behind chatbots and how knowledge graphs help to optimize chatbot conversations? Check out our whitepaper.
Kauz Chatbot World 2021 — Best practices On Chatbot Deployment For Enterprises
At this half-day event, participants can get up-to-date on current developments in chatbot development. Through various practical examples, participants will gain insights into how chatbots can be used in customer service or user support. And the best part: It’s completely free of charge!
The most important information about Kauz Chatbot World 2021 at a glance:
- Date: 10th March 2021
- Location: Online
- Website: Here you can find more information about Kauz Chatbot World 2021.
ai-zurich Conference 2021 — Artificial Intelligence In Business
This event focuses on Artificial Intelligence in Business. There will not only be numerous interesting presentations about this topic, but also a variety of networking opportunities. Also exciting: The event is being held as a hybrid event. Who gets an on-site ticket will be decided by the Artificial Intelligence KAIA.
Trending Bot Articles:
1. How Chatbots and Email Marketing Integration Can Help Your Business
The most important information about the ai-zurich Conference 2021 at a glance:
- Date: 06th May 2021
- Location: Online and in Zurich (Switzerland)
- Website: Here you can find more information about the ai-zurich Conference 2021.
3rd World Chatbots Summit — Trends And Best Practices In AI And Chatbot Development
The focus of the third World Chatbots Summit is on best practices for implementing NLP tools, selecting relevant bot KPIs, as well as privacy and chatbot security. In addition to numerous expert presentations, networking opportunities will not be neglected in this two-day hybrid event.
The most important information about the 3rd World Chatbots Summit at a glance:
- Date: 03rd to 04th June 2021
- Location: Online and in Berlin (Germany)
- Website: Here you can find more information about the 3rd World Chatbots Summit.
Ai4 2021 — Cross-industry Use Of Artificial Intelligence
At Ai4, executives and data experts come together to discuss the challenges and potentials of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning. This event aims to provide practical insights and food for thought about what the use of Artificial Intelligence means for different industries.
The most important information about Ai4 2021 at a glance:
- Date: 17th to 19th August 2021
- Location: Online
- Website: Click here for more information on Ai4 2021.
Data Science Saloon Virtual — AI And Machine Learning In Retail And E-Commerce
As a hybrid event, the Data Science Saloon brings together specialists from retail and e-commerce to share best practices, collaborate on new solutions, and learn about industry trends through webinars and live training sessions.
The most important information about the Data Science Saloon Virtual at a glance:
- Date: 25th August 2021
- Location: Online
- Website: Click here for more information on the Data Science Saloon Virtual.
Shift/CX Online Conference — Chatbots And Conversational Marketing
The Shift/CX Online Conference invites you to a digital experience exchange on the topic of Chatbots and Conversational Marketing. This online event focuses primarily on current trends and experiences from the field, as well as networking opportunities.
The most important information about the Shift/CX online conference at a glance:
- Date: 06th October 2021
- Location: Online
- Website: Click here for more information on the Shift/CX Online Conference.
Did we miss any important events? Feel free to email us. To learn more about Onlim’s Conversational AI platform for automating customer communication, visit our homepage.
Don’t forget to give us your 👏 !



Virtual Chatbot And Conversational AI Conferences 2021 was originally published in Chatbots Life on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
-
5 Ways To Grow Online Store using WooCommerce Chatbot.
Grow your Online Business by Integrating WooCommerce Chatbot into your Online Store.
Facebook Messenger chatbots can help you by:
1.Showcase your Products
2.Add FAQs
3.Manage Order Status and Abandoned Cart Recovery
4.Automate Feedback
5.Share Offers with your Customers
submitted by /u/Botmywork
[link] [comments] -
9 Best Chatbots in the Financial Services Industry
As user’s expectations grow, AI is playing an increasingly important role in the financial services industry to keep with the expectations. Many financial companies are experimenting with chatbots both for offering new and better financial services to their customers and for general customer service. The chatbots in the finance industry add significant value to the user experience and cost management budgets. In any business, customer support and satisfaction are fundamental pillars. Hence, it is important to build a strong foundation of these pillars to have a successful business. By incorporating AI chatbots in the finance industry, the chatbots can handle routine requests such as balance inquiry, payment information thereby, reducing the workload of call center employees so that they can focus on other challenging tasks and strategies which require a higher degree of expertise.
According to a report from , 90% of customer service leaders agree that personalization is the need of today’s business. It is the future of automation and the next generation CX revolution. In every industry, Chatbots have established themselves as the best tool and helped companies provide more value to the users and reduce business expenses.
A report from business wire says that one-third of customers revealed they would consider switching companies after they experience a single case of poor customer service. To avoid such issues, brands are adopting new ways to provide excellent customer service to their users.

To help you in your venture, we have compiled a list of the top 10 best financial chatbots on various use cases such as:
- Banking and account services
- Customer service agent assistance
- Voice-enabled virtual assistants
- Requesting and managing refunds
- Flexible chatbot platforms for multiple uses
- Self-service insurance transactions
Read on: How personal finance chatbots can help users redefine money management
Best Chatbots in the Finance department
Kasisto:
Kasisto has an AI chatbot platform called KAI. They claim to help financial institutions by creating chatbots for them. The chatbots can be used to make payments, review account details, and ask questions. Kasisto’s chatbots can also help users to manage their funds from multiple accounts. In case the chatbot is unable to solve a customer’s problem, then KAI software can send a chatbot conversation to the customer service department, where the employees take over the task and assist further.
Chatbots of Kasisto’s platform can be integrated into desktops, apps, and dashboards for backend employees. The Chatbots are trained to converse with customers regarding financial tasks. Customers can also schedule and send payments, or update the terms of claims through Chatbots. The software can send a chatbot’s conversation to a human agent in case the bot cannot solve a customer’s problem.
Chatbots developed using Kasisto’s platform can integrate into smartphone apps, websites, and dashboards for backend employees. The company also claims to have a deep learning tool for business banking chatbots that helps train new machine learning models, however, they do not offer a detailed explanation of how multiple neural networks would work to make a chatbot more effective.
Trending Bot Articles:
1. How Chatbots and Email Marketing Integration Can Help Your Business
Tars:
Tars are known for its chatbots templates for every situation and in any industry. Particularly, their chatbot templates in the finance industry are more popular. The other good thing is that Tars have used their chatbots on their website. Working with Tars chatbot doesn’t need any coding experience. The chatbots are programmed in such a way that they immediately catch users’ attention, invite them for a conversation and encourage them to take the required action.
If any company wants a customized chatbot that is made just to solve their problems, Tars can do that too. Tars have a powerful AI integration feature, which can be integrated with any business management application. Tars say that if you use their financial services and banking chatbot then your conversion rate will increase up to 2–3x. Financial services chatbot helps you reduce the retention rate, saves money, and offers personalized engagement with the customers.
Haptik:
Haptik is one of the best emerging Chatbot tools that work on the Smart Skills technology, custom-made for the finance and other industries. Haptik has a rich library of smart skills that are derived from key-learnings and best practices of the financial services industry.
Haptik offers pre-built integrations where the IVA can be effortlessly integrated with other contact center infrastructures like CRM, ticketing systems, and ERP. Haptik has a Native Python-Based code editor that performs all the tasks. The information between the IVA and the other applications can be transferred easily using open APIs, and open, flexible Webhooks.
Haptik’s financial services chatbots can be used across multiple channels such as WhatsApp, SMS, Messenger, Google Business messages and provides seamless integration with IVR systems such as Genesys, Avaya, Zendesk, Freshcaller, Cisco, and more. These chatbots converse in a natural, engaging, and personalized manner across various platforms that make the customer experience delightful. Haptik also helps in maintaining a unified and consistent brand voice across marketing, sales, service, and support.
[Expert guide] — Factors to Consider While Implementing Conversational AI for Financial Services
Hybridchat:
Hybridchat is a live chat software that integrates chatbots and connects them bi-directionally to a messenger that the company prefers. Hybridchat boosts digital adoption and streamlines banking operations and helps in reducing costs by automated FAQs and customer service inquiries by saving time for your customer support team.
It is a self-service software which means the new clients can easily be onboarded on the platform by helping them during the user registration, authentication, and account registration process.
The employees in the financial services industry often have to hear the same questions again and again. To save customer support time, chatbots can answer customer inquiries and help companies to sell everything from credit cards to insurance policies.
Growthbotics:
Growthbotics offer different services like Chat Apps, Whatsapp API, CV, CRM, OCR, Payment Gateway Integration, Discord Bots, Alexa Skills development, Twilio API, WeChat API integration, and AI security.
They offer to reduce employee headcount and operational inefficiencies by 30%. Their chatbots include NLP powered chat support and price/product recommendations.
Growthbotics AML and KYC Automation features can stop fraud. Their AI OCR Image and Recognition detect fraud and automate, compliance, KYC and e-loans.
They help in improving the customer experience with customization AI face and Voice Assistant.
Their AI feature can point out non-paying clients and also find ones with bad credit scores.
Growthbotics make customer onboarding easy with AI sentiment assistants.
Their AI tool helps to recommend products and estimate prices based on data.
Kore:
Some of the key stats that Kore talks about:
- 40% of repetitive accounting and finance tasks can be effectively automated by chatbots.
- A 90% increase in accuracy can be achieved by eliminating the inefficiencies and complexities inherent in traditional accounting processes.
- 50% reduction in payroll costs can be achieved by implementing chatbots to augment your existing finance or accounting staff.
Kore.ai bots help companies in the financial services industry to be more productive and efficient. They make invoicing easier. Their chatbots can be trained in identifying the accounting codes that should be assigned to each type of invoice and automatically update the necessary systems of record. This helps in improving finance visibility, productivity, and cost-effectiveness and reduces the possibility of human error.
Collect.Chat:
Collect.Chat also offers different types of Finance Chatbot Examples and Free Templates for various use cases. The templates can easily be edited, updated, and installed on the finance business website. Some of the templates they offer are:
- Merchant Service
- Insurance Assistant
- Mortgage Survey
- Mortgage Help
Collect.Chat chatbots interact with the customers in a personalized manner that helps in generating leads. These chatbots are proactive and available 24/7 to serve customers. The messaging done by chatbots is 100% automated. Depending upon the user, the bots can easily change the flow of the conversation. Collect.Chat chatbots converse with every visitor and help in capturing emails of the users which can later be used in the lead generation process.
The chatbots can easily be built using a simple drag and drop feature. The conversations can be created with draggable elements. The customer support team will be quickly notified whenever a user finishes a conversation with the chatbot. Chatbots can be used to schedule and book meetings with senior agents. Chatbots made by Collect.Chat is mobile friendly and can easily be used to gather insights on customer satisfaction by asking their opinions & measuring their experience. The bots can easily be shared via social media or in the campaigns with a link that can be used to increase the reach and qualify leads.
Nuance Virtual Assistant
Nuance Communications is popularly known for its AI-enabled voice recognition technology for healthcare. Recently, they started offering services in the financial services industry. They offer a virtual assistant service called Nina. The customers can ask Nina questions by voice or text. The virtual assistant can be integrated into the company’s website or smartphone app. It is compatible with SMS texting applications, smart TVs, or acts as a customer service platform for bigger companies.
New users come across issues while setting up their account which Nina can handle flawlessly just by answering a few questions. Nina can also display highly personalized automatic prompts as per the user behavior. For instance, if a user is spending a long time on a particular financial plan, Nina can be configured to show prompts that offer advice. This way a chatbot like Nina can help navigate the user towards making an informed decision.
Paypal:
Paypal also offers an AI-powered customer service chatbot that can be run through Facebook messenger. For security reasons, Paypal chatbots ask users to log in every time they want to use the application.. The chatbots also bring up a list of the customer’s disputed payments so that the customers can make sure to check the status of each one.
Users can also ask any questions about their Paypal account with chatbots. Common questions include:
Declined payments:
To know the reason why a particular payment was unable to clear or why the users were not able to accept payment that has been sent to them.
Unauthorized charges:
Customers can make inquiries about payments for goods and services that the customer did not purchase, which is followed by how to solve the issue.
Passwords
Passwords section also includes other login information such as the email which is connected with the account and other security questions as well
Account Holds and Limitation
Any condition set on the user’s account that limits how much money they can send or accept and how frequently they are allowed to.
Paypal also claims to use ML technology to detect fraud and risk mitigation on their payments platform. They claim to use hundreds of identifying factors within each transaction to ensure that no suspicious activity is going on. This also includes chatbot interactions like asking certain questions within a particular time frame.
Read On: Why Financial Services Brands Should Leverage Conversational AI for Customer Care
To Sum Up
Finance chatbots can provide support anywhere in the world to any user. They are available 365 days a year and can answer a question 24/7, solve common issues quickly like, resetting a password, managing transactions, or finding the nearest open office. Chatbots can handle multiple requests at a time. They decrease user waiting time and resolution time. Chatbots save 4 minutes per inquiry as compared to traditional call centers.
According to a Juniper study , companies that use virtual agents and chatbots will save $8 billion per annum by 2022. Finance chatbots can help to generate leads, reduce business expenses and turn the leads into buyers. They help reduce the workload and work 24/7.
Want to develop an Intelligent Virtual Assistant solution for your brand?
Don’t forget to give us your 👏 !



9 Best Chatbots in the Financial Services Industry was originally published in Chatbots Life on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
-
5 reasons why every Lawyer needs a Virtual Assistant
Virtual Assistants — Next-gen solution to mitigate administrative challenges
Law firms and lawyers managing business in a digitally tech-savvy environment, need to consciously capitalize on emerging automation technologies to better manage their workflow and client experience. Typically, lawyers spend about 40% of their time in scheduling meetings, searching for relevant documents and managing volumes of case history databases. These challenges become exacerbated when handling multiple clients and varying client matters, leading to reduced focus on core business activities. A high level of administrative support needed for the seamless functioning of law firms as well as solo practitioners has made Virtual Assistants a perfect solution for the legal industry. In addition to increased staffing costs, difficulties in acquiring skilled talent and communication channels have left little room for law firms and lawyers to find a cost-effective way to stay ahead of competition. In such challenging scenarios, integrating virtual assistants is the most valuable proposition to gain operational efficiencies and provide best-in-class customer experience.
Virtual assistants facilitate lawyers to perform routine legal tasks more quickly, accurately, and in a cost-effective way. In the absence of relevant security solutions in place, accessing legal documents as well as file sharing have become increasingly challenging for lawyers especially outside the office network, considering privacy and compliance concerns.

Virtual assistants built with text and voice capabilities play an influential role in boosting the productivity of lawyers, by providing secure access to client documents from anywhere and on-the-go, substantially improving mobility. These solutions offer attorneys instant and efficient administrative support by providing access to the right information at the right time and allowing them to focus more on critical work. Virtual assistants also provide additional insights to lawyers in formulating their cases and establishing a strong relationship between the lawyer and the client. To summarize, Virtual assistants have a huge potential to radically change the legal industry by supporting lawyers in delivering better and personalized legal services to their clients. Intelligent virtual assistants are disrupting the traditional legal practice and are aiding lawyers in streamlining operations and helping them remain competitive by minimizing their time spent on monotonous tasks.
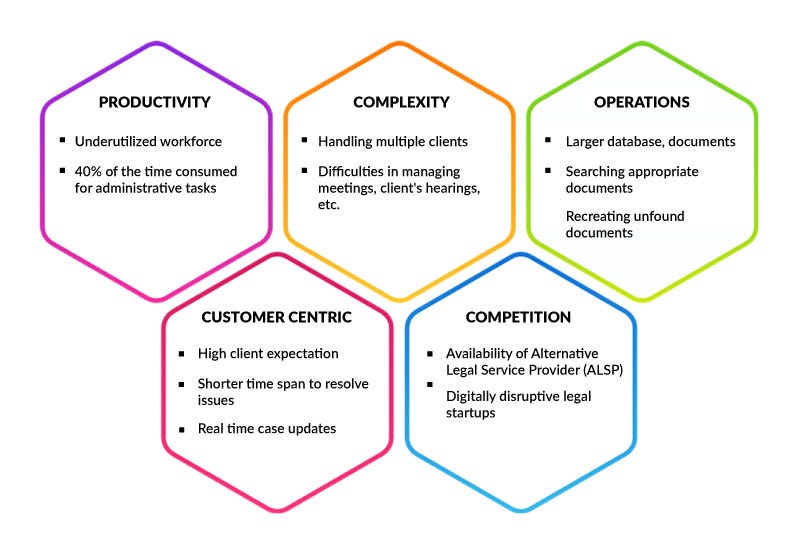
Challenges Faced by Lawyers Domain-specific Virtual Assistants — “Simplifying Matters” for Lawyers
While intelligent assistants in smart devices (smart speakers, smartphones) are gaining popularity and gradually being adopted by lawyers, they still need to deal with a variety of challenges and associated risks. These devices integrated with AI assistants pose numerous Security & Privacy issues for lawyers. The key functionality of these devices is to capture and store all transcripts and data on external servers or cloud, resulting in Loss of privacy as well as Loss of control for lawyers. These smart devices are not built with enterprise-grade security and have weak authentication, making them easier to hack allowing access to client data and other sensitive legal information.
Lawyers using smart devices for voice search queries must deal with issues of general-purpose assistants, which are typically non-domain specific, resulting in poor user experience. These voice assistants in smart devices often skip interpreting legal-domain specific words that restrict the search results to be more precise.
5 Major Reasons Why Lawyers Should Integrate KLoBot’s Virtual Assistants
More Secure and Compliant
Privacy and data security are major concerns for lawyers, especially with reference to confidential data of clients. KLoBot’s virtual assistant is compliant with data privacy regulations, offering secure transcription services and feature-rich admin console, which strengthen the document security as well as secure access for lawyers. KLoBot’s virtual assistant understands the legal industry contextually, reducing complexity in accessing the relevant information securely as well as enabling on-the-go agility. The enhanced mobility also helps while sharing documents with other colleagues across different channels.
Trending Bot Articles:
1. How Chatbots and Email Marketing Integration Can Help Your Business
Automated meeting coordination
KLoBot’s virtual assistant supports lawyers in managing their day to day activities, including scheduling appointments, setting reminders, and other basic tasks. Coordinating calendars and organizing meetings are time-consuming as well as cumbersome for lawyers as they are often reliant on other junior professionals for scheduling important meetings. In addition, KLoBot’s virtual assistant provides automated meeting coordination, resulting in reduced scheduling time and efficiently organized calendars.
Handling customer interactions
KLoBot’s intelligent virtual assistant can handle client interactions by “humanizing” communication through text and voice. The solution can connect with clients, personalizing their experience and provide reminders related to case hearings, meetings, and other case details. Lawyers handle repeated client queries and provide legal advice for the same issues to different clients, which hampers their productivity. KLoBot’s virtual assistant handles FAQs and manages client queries, which reduce the workload of lawyers. KLoBot’s “People Search” helps prospective clients to quickly and efficiently check the lawyer’s or law firm’s expertise. This enables faster access to right the lawyer with the necessary capability and expertise as well as helps in generating targeted leads.
Legal Search
KLoBot’s virtual assistant is helping lawyers to search for important documents, contracts, and other materials of specific cases on-the-go using text as well as voice.
The intelligent virtual assistant can sort through legal documents from voluminous records, allowing lawyers to retrieve old case information. For Instance, KLoBot’s solution “netDocShare” a cloud-based document management service, provides lawyers with access to NetDocuments content on SharePoint by using KLoBot’s text and voice-enabled virtual assistant.
Enabling Smart Offices
Other than FAQs, every client has unique legal requirements that need to be addressed. KLoBot’s virtual assistant is enabling smart law firms that provide lawyers ease of usability, better control over resources, streamlining their practice and promptly assisting clients in resolving their legal issues. KLoBot’s virtual assistant ensures the security of confidential files even in external environments, which makes sharing documents significantly easier. By supporting lawyers in efficiently carrying out basic tasks, KLoBot’s virtual assistant augments operational capabilities resulting in improved productivity.
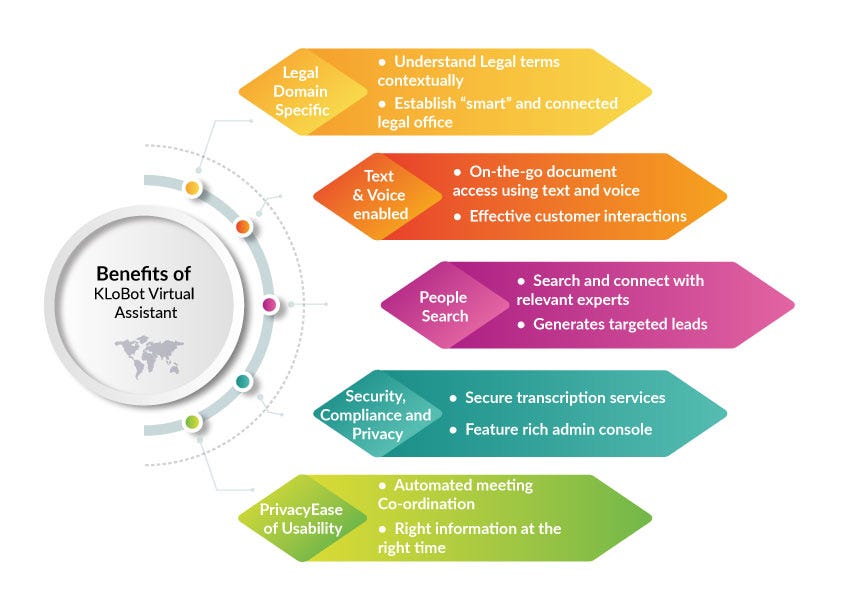
Benefits of using KLoBot Virtual Assistant Don’t forget to give us your 👏 !



5 reasons why every Lawyer needs a Virtual Assistant was originally published in Chatbots Life on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
-
3 COMMON USE CASES A CHATBOT CAN HELP YOUR BUSINESS/WORK EASILY RESOLVE
The Chatbot Market was projected to grow from $2.6billion in 2019 to $9.6billion by 2024.* In 2020 however, the market valuation reached $17.17billion**, almost double of what it was projected to in 4 years due to the impact and resultant demand brought about by the global pandemic. A good number of businesses globally and even locally in Nigeria and Africa resorted to Chatbots to handle the extra work load and the market is now expected to be valued at $109billion by 2026.
But Chatbots, and indeed, every other technology is not a one size fits all that we should just adopt blindly and expect to results instantly. No, that would be unwise.
Here are 3 problems or instances that if you experience in your work or business, a Chatbot would definitely help to resolve.

Lots of Repetitive Requests Or Tasks: Repetitive, mundane and boring tasks tend effect a person’s productivity in unexpected ways. Aside from being a poor use of productive time, people tend to make mistakes when they do and expect to do a task over and over again. This often leads to diminishing returns for the person’s output. Chatbots are commonly used to automate these kinds of processes; Whether they are frequently asked questions, or sending a type of message or file, one of the best decisions you can make for your business is to introduce a chatbot to help out with that part of your operations.
Lead Generation: Chatbots are often used to ask questions that can help qualify your leads to know which ones are cold, warm or even hot. You can then pass the most promising ones to your sales reps to follow up while you send automated messages to further nurture the warm and cold ones. According to a study by Lead Connect, 78% of customers buy from the company that responds to their inquiry first.
Trending Bot Articles:
1. How Chatbots and Email Marketing Integration Can Help Your Business
Absenteeism: No matter how hardworking or hands-on we are in our work or business, there are moments which we may not be available to answer the requests or inquiries of our customers. In today’s on-demand world where everyone wants things in the now, now now, a 5 minute plus delay in responding to a request can lead to up to 80% reduction in chances of qualifying the lead according to a study done by Drift. A chatbot can help stand in the gap for those moments where you or your staff are not available to respond to an enquiry (such as during closing hours or weekends). You can integrate to your email calendar and instantly schedule a meeting right from your bot.
So do you any questions or comments around chatbots? Feel free to ask below and I will do my best to answer.
(* Source: Artificial Solutions: State of Chatbot report 2019)
(** Source: Researchandmarkets.com Chatbot market report)
Don’t forget to give us your 👏 !



3 COMMON USE CASES A CHATBOT CAN HELP YOUR BUSINESS/WORK EASILY RESOLVE was originally published in Chatbots Life on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
-
Reasons Why Chatbots are Important in CRM?
CRM needs to be a functional unit in any corporate setup. Moreover, the companies’ additional services, such as implementing CRM bots, are considered an excellent way to optimize the relationship. Hence, adopting a chatbot for customer service is the best thing to do for new and budding businesses. Take a step ahead with BotPenguin; after all, customer satisfaction makes a company strive in the market. Here is the detailed blog.
submitted by /u/botpenguin1
[link] [comments]

